New techniques in QR-based phishing campaigns evade traditional scanners, highlighting the need for integrated AI defenses
Barracuda Networks, a global cybersecurity leader, has uncovered a sophisticated wave of QR code phishing attacks, known as ‘Quishing’, where cybercriminals are using split and nested QR codes to evade detection. The findings come from Barracuda’s latest threat analysis, revealing that attackers are constantly innovating to bypass traditional security controls.
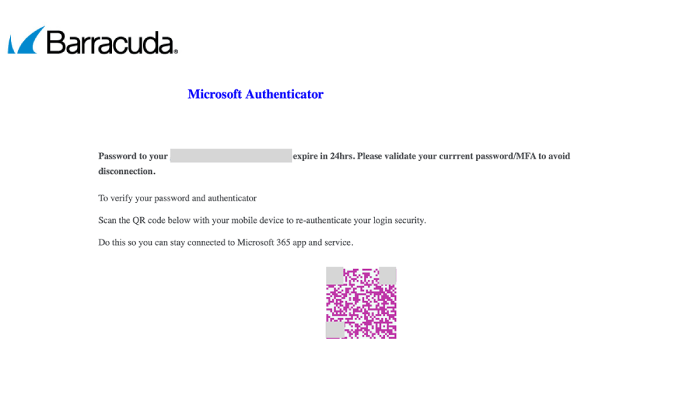
Quishing leverages QR codes embedded with malicious links that redirect victims to fake websites designed to steal credentials or sensitive information. In recent campaigns, Barracuda analysts observed two new tactics:
- Split QR codes: Attackers divide a single malicious QR code into two images placed side by side, appearing normal to the human eye but evading email security scanners. The Gabagool phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) kit used this method in fake Microsoft password reset scams.
- Nested QR codes: Malicious codes are wrapped around legitimate QR codes, creating ambiguity for scanners. Tycoon PhaaS implemented this technique, directing the outer QR code to a phishing site while the inner QR code linked to Google.
“Attackers are innovating with split and nested QR codes to bypass traditional security, taking users outside the corporate perimeter. AI-powered, multi-layered protection is essential to stay ahead.” – Saravan Mohankumar, Manager, Threat Analysis, Barracuda
“Malicious QR codes are attractive to attackers because they look legitimate and bypass standard filters. Since users often scan them on mobile devices, they are outside company protections, making these attacks harder to detect and prevent,” said Saravan Mohankumar, Manager, Threat Analysis, Barracuda.
To defend against these evolving threats, Barracuda recommends a combination of security awareness training, multi-factor authentication, robust spam filters, and multi-layered email protection powered by multimodal AI. This approach allows organizations to detect, decode, and inspect malicious QR codes in real time, even when the embedded content is obscured.